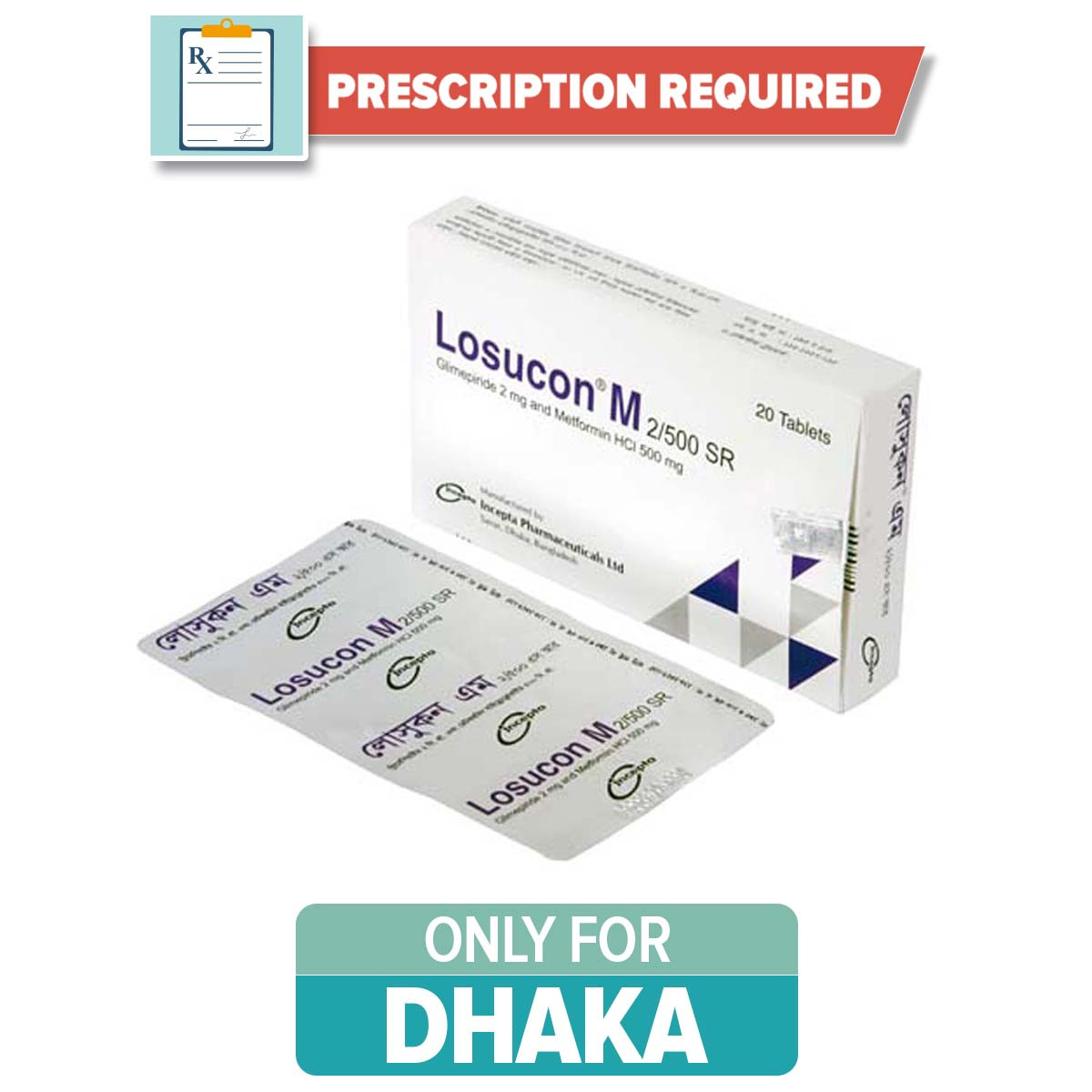

Losucon M 2/500 SR Tablet (10pic)
Inhouse product
-
৳1,030.00
৳1,550.00 -
৳10.00
৳12.00 -
৳280.00
৳500.00 -
৳127.00
৳132.00 -
৳900.00
৳1,300.00 -
৳112.00
৳120.00
Reviews & Ratings
Generic
Glimepiride + Metformin
Indications
In type 2 diabetes mellitus patients, this pill is suggested as an addition to diet and exercise. –
- If glimepiride or metformin monotherapy does not result in sufficient glycemic control.
- Replacement of glimepiride and metformin combo treatment.
Pharmacology
Glimepiride is a sulfonylurea anti-diabetic medication that lowers blood glucose levels. Glimepiride's principal mode of action appears to be based on increasing the release of insulin from active pancreatic beta cells. Glimepiride works in tandem with glucose to increase beta cell sensitivity to physiological glucose stimulation, resulting in insulin production. Glimepiride's action may also be influenced by extrapancreatic effects such as reduced baseline hepatic glucose production, enhanced peripheral tissue sensitivity to insulin, and glucose absorption. A single dosage of Glimepiride has a 24-hour hypoglycemic effect in non-fasting diabetic individuals.
Metformin Hydrochloride is an oral antihyperglycemic medication of the biguanide class that is used to treat type 2 diabetes. It reduces both basal and postprandial plasma glucose levels. It has a different mode of action than sulfonylureas and does not cause hypoglycemia. Metformin Hydrochloride reduces hepatic glucose synthesis, lowers intestinal glucose absorption, and increases insulin sensitivity by increasing peripheral glucose uptake and utilization.
Dosage
- The dosage of this tablet is governed by the desired blood glucose level. The dosage of this tablet must be the lowest which is sufficient to achieve the desired metabolic control. During treatment with this tablet glucose levels in blood and urine must be measured regularly.
- Mistakes, e.g. forgetting to take a dose, must never be corrected by subsequently taking a larger dose.
- As an improvement in control of diabetes is, in itself, associated with higher insulin sensitivity, glimepiride requirements may fall as treatment proceeds. To avoid hypoglycaemia timely dose reduction or cessation of this tablet therapy must therefore be considered.
- The highest recommended dose per day should be 8 mg of glimepiride and 2000 mg of metformin.
- In order to avoid hypoglycaemia the starting dose of this tablet should not exceed the daily doses of glimepiride or metformin already being taken.
- When switching from combination therapy of glimepiride plus metformin as separate tablets, this combination should be administered on the basis of dosage currently being taken.
Administration
This tablet must be swallowed whole and not crushed or chewed.
Interaction
In the case of Glimepiride:
- Glimepiride is metabolized by cytochrome P450 2C9 (CYP2C9). This should be taken into account when glimepiride is coadministered with inducers (e.g. rifampicin) or inhibitors (e.g. fuconazole) of CYP 2C9.
- Potentiation of the blood-glucose-lowering efect and, thus, in some instances hypoglycaemia may occur when one of the following drugs is taken, for example: insulin and other, oral antidiabetics; ACE inhibitors; anabolic steroids and male sex hormones; chloramphenicol; coumarin derivatives; cyclophosphamide; disopyramide; fenfuramine; fenyramidol; fbrates; fuoxetine; guanethidine; ifosfamide; MAO inhibitors; miconazole; fuconazole; para-aminosalicylic acid; pentoxifylline (high dose parenteral); phenylbutazone; azapropazone; oxyphenbutazone; probenecid; quinolones; salicylates; sulfnpyrazone; clarithromycin; sulfonamide antibiotics; tetracyclines; tritoqualine; trofosfamide.
- Weakening of the blood-glucose-lowering efect and, thus raised blood glucose levels may occur when one of the following drugs is taken, for example: acetazolamide; barbiturates; corticosteroids; diazoxide; diuretics; epinephrine (adrenaline) and other sympathomimetic agents; glucagon; laxatives (after protracted use); nicotinic acid (in high doses); oestrogens and progestogens; phenothiazines; phenytoin; rifampicin; thyroid hormones.
- H2 receptor antagonists, beta-blockers, clonidine and reserpine may lead to either potentiation or weakening of the blood-glucose-lowering efect. Under the infuence of sympatholytic drugs such as beta-blockers, clonidine, guanethidine and reserpine, the signs of adrenergic counter-regulation to hypoglycaemia may be reduced or absent.
- Both acute and chronic alcohol intake may potentiate or weaken the blood-glucose-lowering action of glimepiride in an unpredictable fashion.
- The efect of coumarin derivatives may be potentiated or weakened.
- Bile acid sequestrant: Colesevelam binds to glimepiride and reduces glimepiride absorption from the gastrointestinal tract. Glimepiride should be administered at least 4 hours prior to colesevelam.
Concomitant usage of Metformin is not advised:
- Alcohol: Alcohol intoxication is associated with an increased risk of lactic acidosis, particularly in case of fasting, malnutrition or hepatic insufciency. Avoid consumption of alcohol and alcohol-containing medications
- Iodinated contrast agents: Metformin must be discontinued prior to, or at the time of the imaging procedure and not restarted until at least 48 hours after, provided that renal function has been re-evaluated and found to be stable.
- Combinations requiring precautions for use: Some medicinal products can adversely afect renal function which may increase the risk of lactic Acidosis. When starting or using such products in combination with metformin, close monitoring of renal function is necessary. Glucocorticoids, beta-2-agonists, and diuretics have intrinsic hyperglycemic activity. Inform the patient and perform more frequent blood glucose monitoring. ACE-inhibitors may decrease the blood glucose levels. Metformin may decrease the anticoagulant efect of phenprocoumon. Therefore, a close monitoring of the INR is recommended. Levothyroxine can reduce the hypoglycemic efect of metformin. Monitoring of blood glucose levels is recommended, especially when thyroid hormone therapy is initiated or stopped, and the dosage of metformin must be adjusted if necessary.
Organic cation transporters (OCT): Metformin is a substrate for both OCT1 and OCT2 transporters. Metformin in combination with:
- Inhibitors of OCT1 (such as verapamil) may reduce efcacy of metformin.
- Inducers of OCT1 (such as rifampicin) may increase gastrointestinal absorption and efcacy of metformin.
- Inhibitors of OCT2 (such as cimetidine, dolutegravir, ranolazine, trimethoprime, vandetanib, isavuconazole) may decrease the renal elimination of metformin and thus lead to an increase in metformin plasma concentration.
- Inhibitors of both OCT1 and OCT2 (such as crizotinib, olaparib) may alter efcacy and renal elimination of metformin.
When these medications are coadministered with metformin, caution is advised, especially in individuals with renal impairment, since metformin plasma levels may rise. Metformin dosage modification may be necessary if OCT inhibitors/inducers affect metformin efficacy.
Contraindications
In the case of Glimepiride-
- In patients hypersensitive to glimepiride, metformin, other sulfonylureas, other sulfonamides, or any of the excipients of Amaryl M.
- In pregnant women.
- In breastfeeding women.
There has been no experience with the use of glimepiride in individuals with severe liver function impairment or dialysis patients. Changeover to insulin is indicated in individuals with significant hepatic function impairment, not least to establish optimum metabolic management.
In the case of metformin-
- Hypersensitivity to metformin or any of the excipients.
- Any type of acute metabolic acidosis such as lactic acidosis Diabetic ketoacidosis, diabetic pre-coma.
- Severe Renal failure or renal disfunction (e.g., serum creatine levels >135 μmol/L in males and >110 μmol/L in females), GFR < 30 mL/min.
- Acute conditions with the potential to alter renal function such as Dehydration, severe infection, intravascular administration of iodinated contrast agents etc.
- Acute or chronic disease which may cause tissue hypoxia such as cardiac or respiratory failure, recent myocardial infarction, shock
- Hepatic insufciency.
- Acute alcohol intoxication, alcoholism.
Side Effects
Hypoglycaemia, temporary visual impairment, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, abdominal pain, urticaria & fall in blood pressure.
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy-
Glimepiride: Glimepiride should not be used during pregnancy. Otherwise, the youngster is in risk of being harmed. During pregnancy, the patient must switch to insulin. Patients who intend to become pregnant must notify their doctor. It is advised that such patients switch to insulin.
Metformin: Diabetes should not be treated with metformin when the patient intends to become pregnant or during pregnancy, but insulin should be used to keep blood glucose levels as close to normal as possible in order to reduce the risk of fetal malformations associated with abnormal blood glucose levels.
Lactation-
Glimepiride should not be used by breast-feeding mothers to avoid inadvertent consumption with breast milk and potential damage to the kid. If required, the patient must switch to insulin or discontinue nursing.
Metformin is secreted in breast milk by nursing rats. Similar results in humans are not available, and a choice should be taken whether to cease breastfeeding or metformin, taking into account the compound's value to the mother.
Precautions & Warnings
For Glimepiride: In the initial weeks of treatment, the risk of hypoglycemia may be increased and necessitates especially careful monitoring. If risk factors for hypoglycemia are present, it may be necessary to adjust the dosage of glimepiride or the entire therapy. This also applies whenever illness occurs during therapy or the patient's life-style changes. It is known from other sulfonylureas that, despite initially successful countermeasures, hypoglycaemia may recur. Patients must, therefore, remain under close observation. Severe hypoglycaemia further requires immediate treatment and follow-up by a physician and, in some circumstances, in-patient hospital care. Treatment of patients with G6PD-defciency with sulfonylurea agents can lead to hemolytic anaemia. Since glimepiride belongs to the class of sulfonylurea agents, caution should be used in patients with G6PD-defciency and a non-sulfonylurea alternative should be considered.
Metformin: Patients with hypothyroidism should have their thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels checked on a regular basis. Long-term metformin therapy has been linked to a drop in vitamin B12 blood levels, which can lead to peripheral neuropathy. Vitamin B12 levels should be checked on a regular basis.
Frequently Bought Products
-
৳1,030.00
৳1,550.00 -
৳10.00
৳12.00 -
৳280.00
৳500.00 -
৳127.00
৳132.00 -
৳900.00
৳1,300.00 -
৳112.00
৳120.00
Online Shopping Bangladesh : MShopBD-Majumder Shop
MShopBD-Majumder Shop Online Shopping in Bangladesh is the Best Shopping store within 10000+ products cash on delivery in dhaka, Khulna, ctg & all over Bangladesh with COD-cash on delivery (Only Shipping Cost Advance ) under by www.esdp.gov.bd (bangladesh.gov.bd ) Home Delivery all Over Bangladesh different location and shop as like as Multivendor Online Sites in BD.
Thank you for choosing MShopBD - Majumder Shop!